The gentle tap of a canine’s tail against the hardwood floor, the soft nuzzle of their muzzle seeking affection—dogs are often considered man’s best friend. They bring joy to our lives with their boundless energy and unwavering loyalty. However, as much as we love them, it is crucial that we remain vigilant about their health, including subtle signs that could indicate an underlying issue. One such sign that should not be overlooked is pale or white gums in dogs. This seemingly innocuous change in color may signal a variety of health concerns, ranging from minor ailments to more serious conditions. In this article, we delve into the significance of dog gum color, its potential causes, and what pet owners must do when they notice these changes.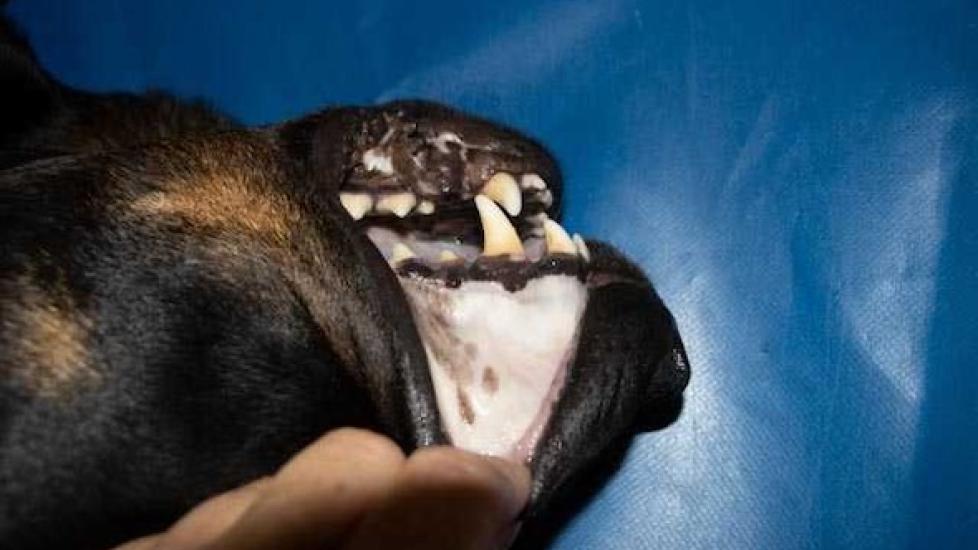
Understanding Canine Gum Health:
Dogs have four main types of tissue within their mouths: gingiva (gums), alveolar bone (which supports the teeth), cementum (a layer on the tooth root), and enamel (the hard outer coating of the tooth). The gums typically appear pinkish-red due to a good supply of blood vessels underneath. When your furry companion’s gums start to look paler than usual, it might be a cause for concern.
Common Causes of Pale or White Gums in Dogs:
1. Anemia: A deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin can lead to pallor in the gums. This condition reduces oxygen transport throughout the body, potentially affecting multiple organs.
2. Blood Disorders: Diseases like immune-mediated hemolytic anemia or thrombocytopenia can affect the production or function of blood components, leading to abnormalities in gum color.
3. Liver Disease: As the liver plays a pivotal role in filtering toxins and producing clotting factors, any impairment can manifest through discoloration of the gums. Jaundice, which also affects the skin and eyes, can sometimes include paleness of the oral cavity.
4. Kidney Failure: Renal issues can result in waste products accumulating in the bloodstream, causing a buildup of uremic toxins that may alter the hue of the gums.
5. Oral Infections: Bacterial infections or dental disease can trigger inflammation, which might temporarily whiten the gums around affected areas.
6. Lack of Vitamins and Minerals: Deficiencies in certain vitamins or minerals, particularly vitamin C, iron, or folate, can contribute to anemic symptoms and thus paler gums.
7. Allergies: Sometimes, allergic reactions can induce swelling or irritation in the mouth, which might influence the appearance of the gums.
What to Do If You Notice Changes in Your Dog’s Gums:
If you observe any deviation from your dog’s normal gum color, take immediate action by scheduling an appointment with your veterinarian. During the visit, expect a thorough examination, possibly involving blood tests, urinalysis, imaging studies, or other diagnostic procedures to determine the exact cause of the problem. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and better outcomes.
Prevention and Care Tips:
To maintain healthy gums and overall well-being, follow these guidelines:
– Regularly brush your dog’s teeth to prevent plaque buildup and subsequent gum disease.
– Offer chew toys or treats designed to clean their teeth.
– Feed a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
– Monitor water intake and ensure access to fresh, clean drinking water at all times.
– Schedule regular check-ups with your vet to detect problems early.
In conclusion, while a change in your dog’s gum color might seem trivial, it could be indicative of a larger health issue. Stay attentive to these subtle cues and act promptly. By doing so, you can provide the care necessary to keep your beloved canine companion happy and healthy for many years to come.
