Understanding Tooth Fractures in Canine Companions: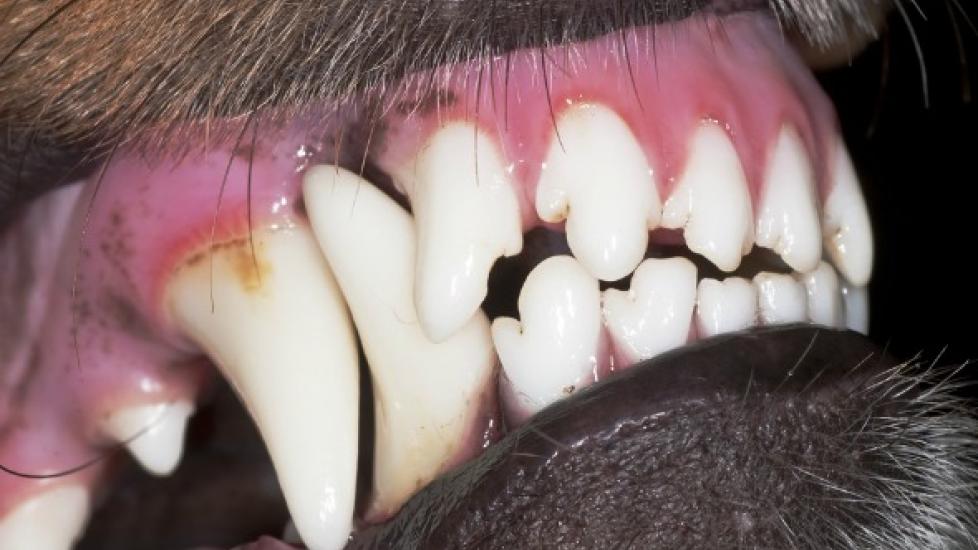
Dogs, like humans, can experience tooth fractures due to various reasons. These dental injuries not only cause discomfort but also pose potential health risks if left untreated. It is crucial for dog owners to be aware of the causes and symptoms of tooth fractures, as well as the importance of seeking veterinary care promptly. In this article, we delve into the topic of tooth fracture in dogs, providing insights on how to identify signs of trouble and what steps should be taken to ensure your furry friend’s oral health.
Causes of Tooth Fractures in Dogs:
- Age-Related Wear: Just as people develop dental issues with age, older dogs may suffer from wear and tear on their teeth. Enamel erosion or gum recession can make teeth more susceptible to breakage.
- Trauma: Accidents such as chewing on hard objects, biting into bones that are too tough, or even playing rough can lead to sudden trauma and subsequent tooth damage.
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): Some dogs exhibit involuntary grinding of their teeth, which can gradually weaken the structure of the enamel over time.
- Periodontal Disease: Advanced periodontal disease leads to inflammation around the roots of the teeth, making them unstable and prone to fracturing.
- Inherited Factors: Certain breeds have a higher predisposition to dental problems due to genetic factors.
Signs Your Dog May Have a Broken Tooth:
- Sensitivity: Your pet might avoid using the affected mouth area when eating or yelp upon contact with food.
- Swelling: There could be swelling around the gums where the broken tooth is located.
- Bad Breath: An increase in bad breath may indicate an infection related to the damaged tooth.
- Difficulty Eating: If your dog seems hesitant to eat normally or has difficulty chewing, it could be a sign of pain associated with a broken tooth.
Importance of Veterinary Care:
It is essential to bring your dog to the veterinarian immediately upon noticing any of these signs. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and reduces the likelihood of further complications. The vet will perform a thorough examination, including X-rays if necessary, to determine the extent of the injury and recommend the best course of action. Depending on the severity of the fracture, treatments may range from simple extraction to complex surgical procedures involving dental implants or bone grafts. Regardless of the approach, timely intervention is key to minimizing discomfort and maintaining overall wellness.
Prevention Strategies:
To reduce the risk of tooth fractures in your beloved pooch:
- Provide appropriate chew toys designed for your dog’s size and jaw strength.
- Regularly check your pet’s teeth for signs of decay or abnormal wear.
- Offer soft foods if you suspect a recent trauma until the situation is assessed by a professional.
- Keep up with regular dental cleanings at home—brushing daily or weekly, depending on your vet’s advice.
- Consider dietary modifications to prevent excessive tartar buildup and promote healthy gums.
Conclusion:
By staying vigilant about our pets’ dental health and being proactive in addressing concerns, we can help maintain their quality of life and keep those wagging tails going strong through all stages of their lives. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are paramount in managing tooth fractures effectively in our canine companions.
